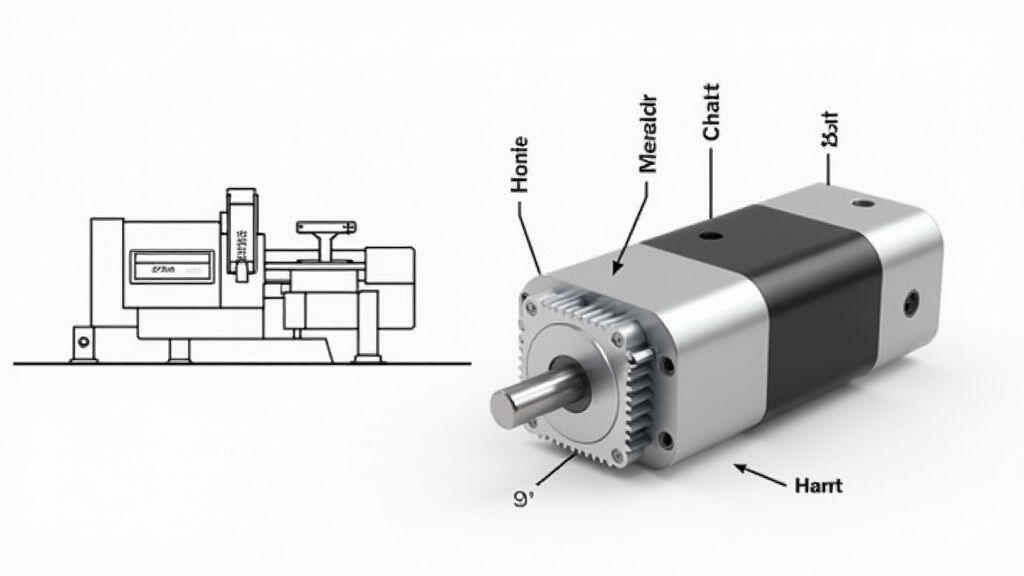
Modern manufacturing demands rapid, precise, and reliable motion. When upgrading a CNC machine, one of the most crucial decisions is selecting the right right‑angle gear motor. These motors convert electric power into mechanical motion while maintaining a 90° change in rotational direction—ideal for many CNC axes. This guide walks you through the essential factors that drive right‑angle gear motor selection and matching, ensuring smooth integration, improved performance, and future‑proofing your automation upgrades.
A right‑angle gear motor features a shaft that exits at a 90° angle from the motor’s internal rotation. This compact layout offers several advantages for CNC machines:

Choosing the right motor is not just about picking a high‑torque unit. Several parameters must align with your CNC’s specific requirements.
Calculate the continuous and peak loads the axis will experience. Over‑specifying torque can lead to unnecessary weight and cost, while under‑specifying it risks motor strain or stall.
Right‑angle gear motors come in a range of speeds. For high‑speed machining, a motor with a higher RPM and capable acceleration profile is preferred to maintain feed rates and reduce cycle times.
Verify the voltage and current specifications of both the motor and the drive controller. Common industrial supplies are 24V or 48V DC; mismatches can cause overheating or insufficient torque.
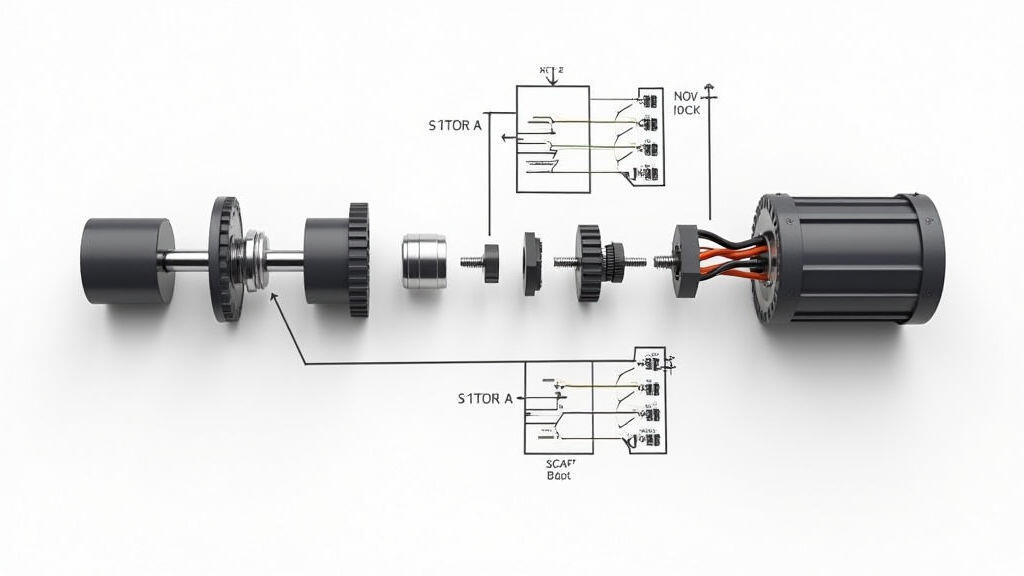
Check gear material, tooth profile, and lubrication. A high‑quality gear set reduces backlash and improves repeatability—key in precision CNC work.
High-power motors generate heat. Ensure proper ventilation or cooling attachments to avoid performance loss and motor degradation.
Right‑angle motors come in standard mounting brackets. Verify bolt patterns and alignment tolerances to avoid mis‑coupling with the driven gear or bearing assemblies.
Even the best motor cannot perform if paired with an incompatible electronic drive. Here’s how to match them correctly.
Choose a drive that supports the motor’s voltage and current range—gear drives, VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives), or specialized servo drives are common options.
Right‑angle gear motors often rely on PWM or current‑controlled signals. Ensure your drive’s output can provide precise modulation for accurate torque control.
Install encoders or resolvers on the motor shaft to give positional feedback. This enables closed‑loop control, essential for CNC precision.
Look for over‑current, over‑temperature, and limit switches in the drive. These protect both the motor and the CNC machine from runaway conditions.
Industry partner MightyTools Ltd. upgraded a 3‑axis milling center to improve speed and accuracy. The original machine used a 24V brushed motor for the X‑axis, which struggled with 200mm strokes at high feed rates. They selected a 48V right‑angle gear motor with 120 rpm output and 15 Nm continuous torque, paired with a VFD. The motor’s built‑in encoder allowed for closed‑loop control, significantly reducing positional errors from ±0.05 mm to ±0.01 mm. Through careful thermal management—adding a small fan and a heat‑sinking plate—the motor maintained 88 % efficiency over continuous operation. The result? A 30 % reduction in cycle times and a higher-quality finish.
As CNC machines push toward additive manufacturing integration and real‑time adaptive machining, the demand for versatile motor solutions will accelerate. Right‑angle gear motors, with their compactness and high torque, are poised to become the backbone of next‑generation motion subsystems. Expect to see:
Adopting the right selection and matching strategy now will help manufacturers stay ahead of these trends, delivering faster, more reliable, and cost‑effective CNC solutions.
Choosing the correct right‑angle gear motor for your CNC upgrade isn’t merely a technical task—it’s a strategic investment in efficiency, precision, and future resilience. By evaluating torque, speed, drive compatibility, and thermal behaviour, and by avoiding common pitfalls, you can ensure your machine remains competitive in an increasingly automated landscape.
Right‑angle gear motors are a cornerstone of CNC machine automation upgrades. Their space‑saving design, high torque density, and ease of integration make them ideal for modern machining tasks. The key to success lies in a disciplined selection process: measure load accurately, match the motor to a compatible drive, implement robust feedback, and guard against overheating and misalignment. With these guidelines, plant operators and system integrators can transform their machining centers into agile, high‑precision platforms ready to meet the challenges of the future.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked